大家好,我是花妹儿。
在 Java 编程过程中,我们经常需要将多个字符串拼接到一起,即字符串拼接。
但是,String 字符串是不可变的,它一旦被创建初始化之后,就不能被修改了,我们怎样才能实现字符串拼接呢?或者说,字符串拼接的实现方法都有哪些呢?
这篇文章我们就一起来看看~
什么是字符串拼接
字符串拼接,顾名思义,就是将两个及以上的字符串,组合为一个大的字符串的过程。
在 Java 中,String 类型是不可变的。也就是说,它一旦被创建初始化之后,就不能被修改了。
那么这个时候,我们要如何去实现字符串的拼接效果呢?
在学习 String 类型数据时,我们用到了下图中的一个内存模型。
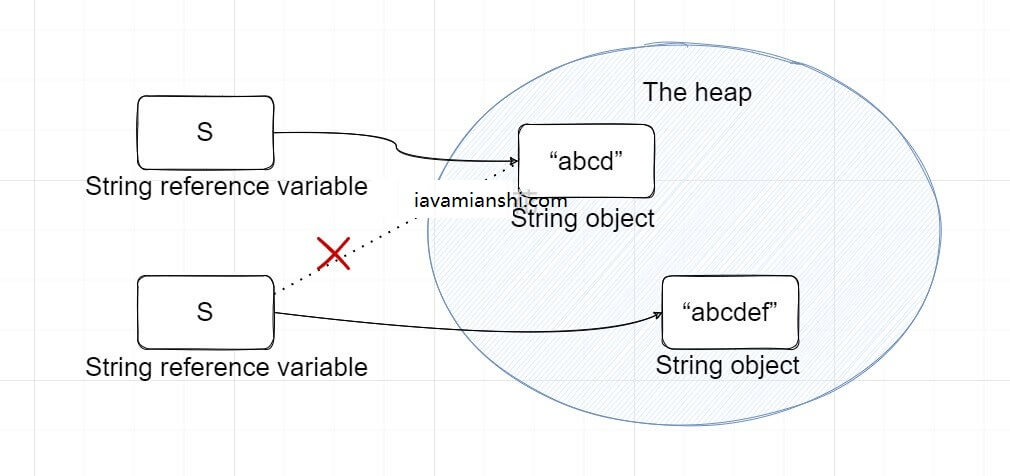
假设:
有两个字符串,字符串 C = “456” 、字符串 D= “789”。
我们要将这两个字符串拼接成一个字符串。
这个拼接操作的过程,其实是创建了一个新的字符串 E=”456789″。
当完成这一系列操作时,字符串“456”,“789”仍然存在于我们的字符串常量池中,等待垃圾回收机制进行回收,新的引用则是指向了新的字符串“456789”。
那么,在 Java 中是怎样实现字符串的拼接呢?
字符串拼接方式
下面这 10 种字符串拼接方式,看看你都用过哪几种。
第 1 种:使用 + 号
这种方法,是我们最容易想到的。
示例代码:
str_1 = 'hello' str_2 = 'world' print(str_1 + ' ' + str_2) # hello world
使用了加号对两个字符串进行拼接,内存模型和上图中的内存模型一样。
第 2 种:使用 % 号
第2种方法是一种格式化字符串的手段,提供很多种格式符来达到“美化”字符串格式的目的。
用起来很简单,也比 + 号使用更灵活,但缺点是可读性相对差,如果 % 号的数量与后面参数的数量不一致,就会报错。
示例代码:
print("%s %s" % ("hello", "world")) # hello world
第 3 种:使用 String 类型的 concat() 方法
示例代码:
public String concat(String str) {
if (str.isEmpty()) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
int otherLen = str.length();
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}
以上,使用了 capy 的方式进行字符串拼接,使用了 new String(buf, true) 操作来创建了一个新的字符串(字符串的不可变性)。
第 4 种:format 格式化
示例代码:
当使用位置作为参数标志时,和 % 的使用方法相似。
print("{0}: {1}".format("hello", "world"))
print("{}: {}".format("hello", "world"))
当需要传多个相同参数的时候,优势就比较明显了。
param = "test"
print("{param} {param} {param}".format(param=param))
第 5 种:使用 str.join(iterable) 方法
字符串自带一个 join(iterable) 方法。
这个方法接受一个可迭代对象,用途是根据一个字符串连接可迭代对象中的字符串。当连接字符串为空时,可以起到无缝拼接的作用。
但是,可迭代对象中的元素必须是字符串类型,否则就会报错。
可迭代对象的内容是字符串类型:
print("".join(["hello", "world"])) # helloworld
print(",".join(["hello", "world"])) # hello,world
可迭代对象的内容不是字符串类型,会报错:
print("".join((1, 2))) # TypeError: sequence item 0: expect
第 6 种:StringBuffer
StringBuffer 是 Java 中用来定义字符串变量的类,通过 StringBuffer 定义的字符串,可以实现扩展、修改等操作。
例如:通过下面这个操作,我们可以将 Hello 和 World 字符串组成 Hello World 字符串。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer stringBUffer = new StringBuffer("Hello");
stringBUffer.append("World");
System.out.println(stringBUffer.toString());
}
}
第 7 种:join 方法
Java8 中,String 类提供了一个 join 方法,功能与 StringUtils 类中的 join方法相似。
示例代码:
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
// Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead.
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
joiner.add(cs);
}
return joiner.toString();
}
第 8 种:使用 string.Template(template) 对象
Template 是 string 模块下的类,它接受一个模板字符串。
主要用于拼接的有两个方法:
- substitute(mapping, **kwds)
- safe_substitute(mapping, **kwds)
这两个方法都接受 mapping 对象,例如:dict,**kwds 是关键字参数,即 k=v 形式的参数。
它们的区别是:当模板字符串中的参数与传入的参数不一致时,substitute() 方法会报错,而 safe_substitute() 方法不会。
示例代码:
from string import Template
# 模板字符串,用 $+关键字 表示
s = Template('$who likes $what')
# 传入关键字参数
print(s.substitute(who='tim', what='kung pao')) # tim likes kung pao
d = {'who': 'tim', 'what': 'kung pao'}
# 传入 mappging 对象
print(s.substitute(d)) # tim likes kung pao
# 将字典当作关键字参数
print(s.substitute(**d)) # tim likes kung pao
d = {'who': 'tim'}
# 当 what 没有对应的值时,如果想不报错,应该使用 safe_substitute
# 它会将 $xxx 原样输出
print(s.safe_substitute(d)) # tim likes kung pao
print(s.substitute(d)) # KeyError: 'what'
第 9 种:使用 ()
代码示例:
tuple_str = ('hello', 'world') # 用逗号隔开,是一个元组
fake_tuple_str = ('hello' ' ' 'world') # 用空格隔开
print(tuple_str) # ('hello', 'world')
print(fake_tuple_str) # hello world
第 10 种:print 多值输出
print('hello' 'world') # helloworld
print('hello', 'world', 'hhh') # hello world hhh
t = "hello"
m = 'world'
print(t, m) # hello world
总结
通过本文,我们了解到了:
- 字符串是不可变的,可以通过新建字符串的操作,来完成字符串拼接。
- 字符串拼接方法有 10 种,分别是: 使用 + 号、使用 % 号、使用 String 类型的 concat() 方法、format 格式化、使用 str.join(iterable) 方法、StringBuffer、join 方法、使用 string.Template(template) 对象、使用 () 拼接、print 多值输出。
- 需要特别注意的是:
- 如果不是在循环体中进行字符串拼接,可以直接使用 + 。(因为在使用 String 循环创建字符串的过程中,一直在创建新的 String 对象)。
- 如果不是并发场景,建议使用 StringBuilder 来进行字符串操作,因为 StringBuilder 拼接字符串的效率最高 ;如果是并发场景,则建议使用 StringBuffer ,因为 StringBuffer 是线程安全的,StringBuilder 是线程不安全的。
以上,是 10 种字符串拼接方式的介绍。

